Understanding Apple Stakeholders: A Comprehensive Analysis
Apple, a global technology giant, owes its success not only to innovative products and a strong brand but also to a diverse group of Apple stakeholders. These individuals and groups have a vested interest in the company’s performance and are affected by its actions. Understanding who these Apple stakeholders are and their respective interests is crucial for anyone looking to grasp the dynamics of the company’s operations and strategic decisions. This article provides a comprehensive analysis of Apple’s stakeholders, exploring their roles, expectations, and influence on the company.
Defining Stakeholders
Before delving into the specifics of Apple’s stakeholders, it’s essential to define the term ‘stakeholder.’ A stakeholder is any individual, group, or organization that can affect or is affected by an organization’s actions, objectives, and policies. This encompasses a wide range of entities, from those directly involved in the company’s operations to those who have a more indirect but still significant connection.
Key Apple Stakeholders
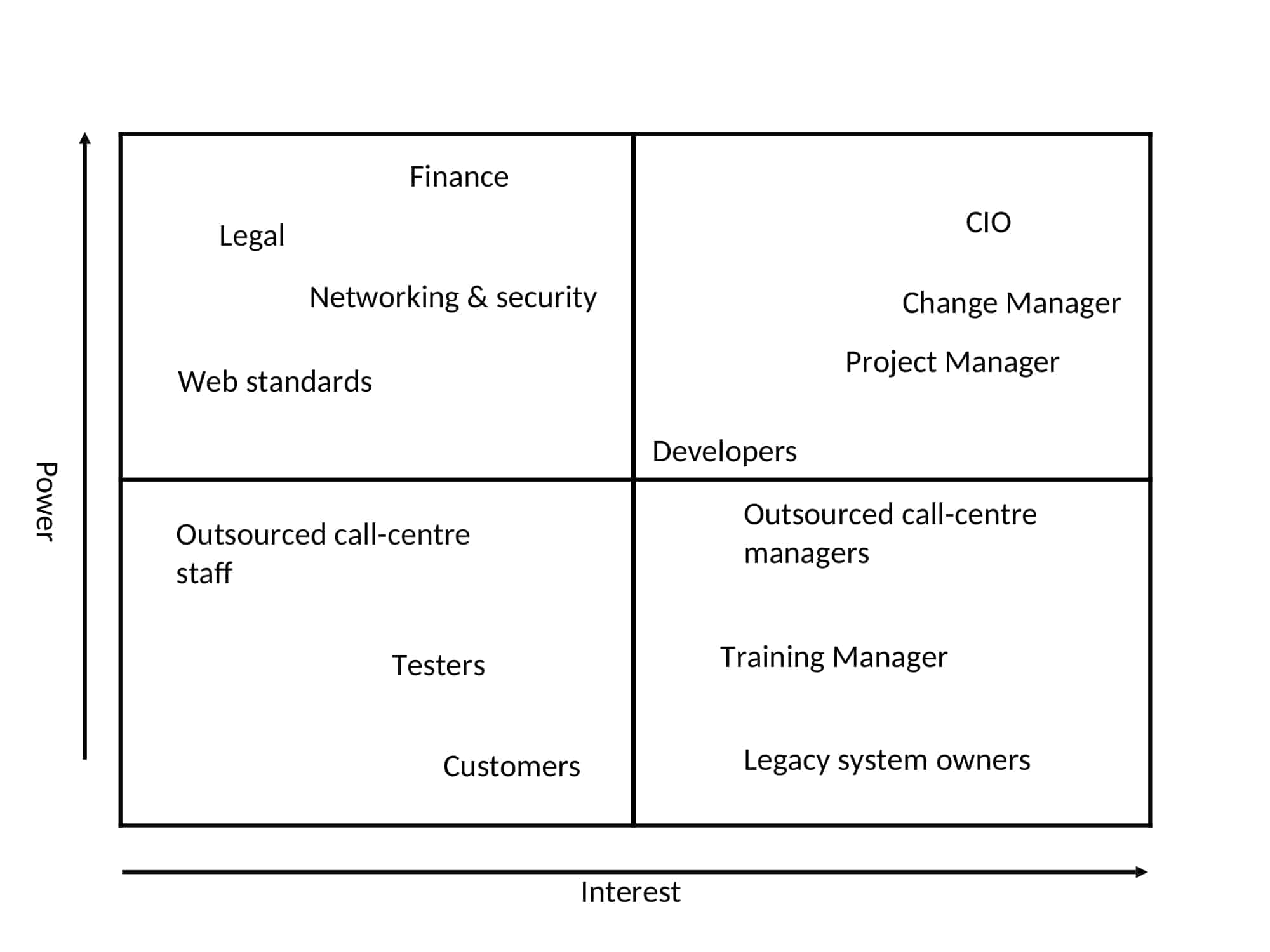
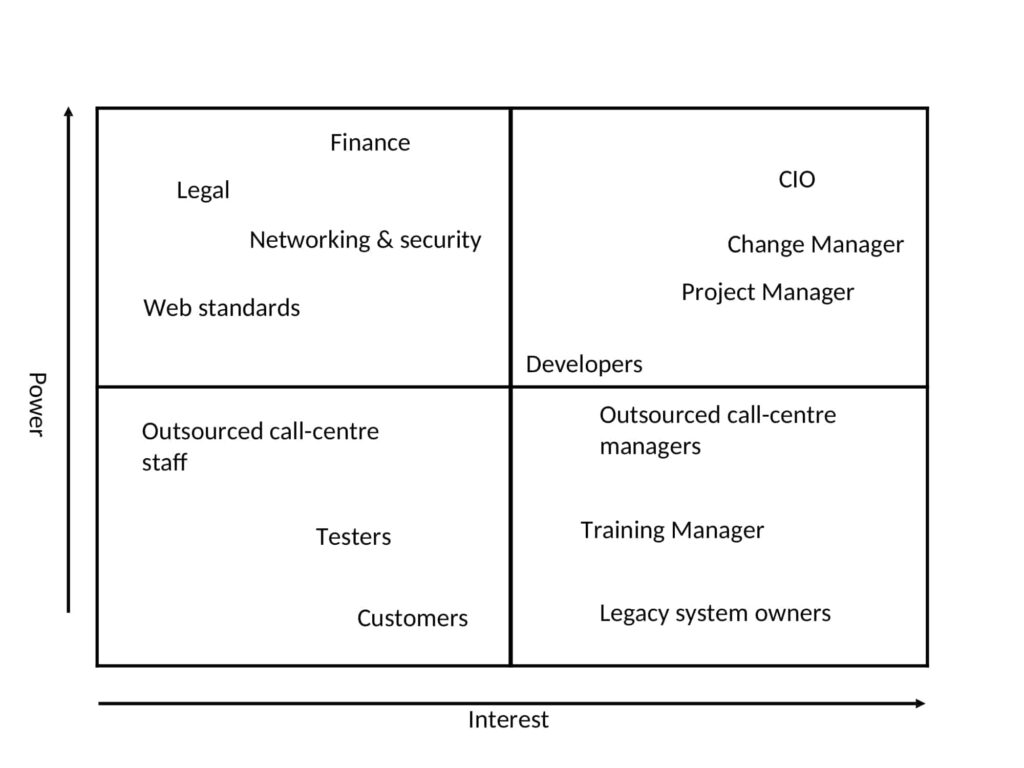
Apple’s stakeholder landscape is complex, comprising several key groups, each with unique interests and expectations. These include:
Shareholders/Investors
Shareholders, also known as investors, are arguably the most influential Apple stakeholders. They own a portion of the company and are primarily interested in its profitability and stock performance. Their investment decisions directly impact Apple’s market capitalization and ability to raise capital for future growth. Shareholders expect Apple to deliver consistent financial results, innovate continuously, and maintain a competitive edge in the market. They also scrutinize the company’s leadership and governance practices. [See also: Apple Stock Analysis: Future Projections and Investment Strategies]
Customers
Customers are the lifeblood of Apple’s business. They purchase Apple’s products and services, generating revenue and driving growth. Apple has cultivated a loyal customer base by consistently delivering high-quality, innovative products and a seamless user experience. Customer expectations are high; they demand cutting-edge technology, reliable performance, and excellent customer support. Maintaining customer satisfaction and loyalty is paramount for Apple’s long-term success.
Employees
Apple’s employees are crucial to its operations, responsible for designing, developing, manufacturing, and marketing its products and services. They are interested in fair compensation, opportunities for career advancement, a positive work environment, and a sense of purpose. Apple strives to attract and retain top talent by offering competitive salaries, benefits, and a stimulating work culture. Employee satisfaction directly impacts Apple’s productivity, innovation, and overall performance.
Suppliers
Apple relies on a global network of suppliers to provide the components and materials necessary for its products. These suppliers are interested in stable contracts, fair pricing, and timely payments. Apple has a significant influence on its suppliers due to its large order volumes. It expects its suppliers to adhere to strict quality standards, ethical labor practices, and environmental regulations. Maintaining strong relationships with key suppliers is critical for Apple’s supply chain efficiency and product quality. [See also: Apple’s Supply Chain Management: Challenges and Strategies]
Government and Regulatory Bodies
Apple operates in a highly regulated environment and is subject to various laws and regulations related to taxation, antitrust, data privacy, and environmental protection. Government and regulatory bodies are interested in ensuring that Apple complies with these regulations and contributes to the economy through job creation and tax revenue. Apple must navigate complex legal and political landscapes to maintain its operations and avoid costly penalties. They are a key Apple stakeholder.
Communities
Apple’s operations have a direct and indirect impact on the communities in which it operates. These communities are interested in Apple’s contributions to the local economy, its environmental impact, and its social responsibility initiatives. Apple invests in community programs and initiatives to support education, environmental conservation, and other social causes. Maintaining positive relationships with local communities is essential for Apple’s reputation and social license to operate.
Competitors
While not traditionally considered stakeholders in the same vein as customers or shareholders, competitors significantly influence Apple’s strategic decisions. Apple constantly monitors its competitors’ products, pricing, and marketing strategies to maintain its competitive edge. The actions of competitors can impact Apple’s market share, profitability, and innovation efforts. In this context, they are considered Apple stakeholders.
The Interplay of Stakeholder Interests
The interests of Apple’s stakeholders are often intertwined and can sometimes conflict. For example, shareholders may prioritize short-term profits, while customers may demand lower prices. Employees may seek higher wages, while suppliers may desire higher prices for their components. Balancing these competing interests is a complex challenge for Apple’s management team. Effective stakeholder management requires understanding the needs and expectations of each group and finding solutions that are mutually beneficial.
Stakeholder Engagement Strategies
Apple employs various strategies to engage with its stakeholders and manage their expectations. These include:
- Investor Relations: Communicating with shareholders through quarterly earnings calls, annual reports, and investor conferences.
- Customer Feedback: Gathering customer feedback through surveys, online forums, and social media channels.
- Employee Communication: Maintaining open communication channels with employees through internal newsletters, town hall meetings, and employee surveys.
- Supplier Collaboration: Working closely with suppliers to ensure quality, ethical labor practices, and environmental compliance.
- Government Affairs: Engaging with government officials and regulatory bodies to advocate for Apple’s interests and ensure compliance with laws and regulations.
- Community Outreach: Supporting community programs and initiatives through philanthropic donations and volunteer efforts.
The Importance of Ethical Considerations
Ethical considerations play a crucial role in Apple’s stakeholder management. Apple is committed to operating with integrity and transparency in all its dealings with stakeholders. This includes adhering to ethical labor practices, protecting customer data privacy, and minimizing its environmental impact. Ethical behavior is essential for maintaining trust and credibility with stakeholders and for ensuring Apple’s long-term sustainability. Apple has faced scrutiny in the past regarding its labor practices at supplier factories and its data privacy policies. Addressing these concerns proactively is vital for maintaining a positive reputation.
Impact of Stakeholders on Apple’s Decisions
Apple’s stakeholders significantly influence its strategic decisions. For instance, pressure from environmental groups has led Apple to invest in renewable energy and reduce its carbon footprint. Customer demand for larger screens and improved camera technology has driven Apple’s product development efforts. Shareholder concerns about executive compensation have prompted Apple to implement performance-based pay structures. These examples illustrate how stakeholder interests can shape Apple’s actions and priorities.
Future Trends in Stakeholder Management
Stakeholder management is an evolving field, and Apple must adapt to emerging trends to remain successful. Some key trends include:
- Increased Transparency: Stakeholders are demanding greater transparency from companies regarding their operations, financial performance, and social impact.
- Focus on Sustainability: Stakeholders are increasingly concerned about environmental sustainability and expect companies to reduce their environmental footprint.
- Emphasis on Social Responsibility: Stakeholders are holding companies accountable for their social impact and expect them to contribute to addressing social issues.
- Digital Engagement: Stakeholders are using digital channels to communicate with companies and express their opinions.
Conclusion
Apple stakeholders are a diverse and influential group that plays a critical role in the company’s success. Understanding their interests, expectations, and influence is essential for anyone looking to grasp the dynamics of Apple’s operations and strategic decisions. By effectively engaging with its stakeholders and addressing their concerns, Apple can build trust, maintain its reputation, and ensure its long-term sustainability. The complex interplay between these Apple stakeholders is a key factor in understanding how the company operates and continues to innovate. Managing these relationships effectively is crucial for Apple to remain a global leader in technology. Recognizing the importance of each Apple stakeholder allows for a more nuanced understanding of Apple’s business strategy and its place in the global market.