How Web Search Engines Work: A Deep Dive into the Digital Information Retrieval Process
In today’s digital age, web search engines are indispensable tools. They allow us to quickly find information from the vast expanse of the internet. But have you ever stopped to wonder how web search engines work? This article delves into the intricate mechanisms that power these digital gatekeepers, providing a comprehensive understanding of the processes involved.
The Core Components of a Search Engine
Web search engines are not monolithic entities. They are complex systems comprised of several key components that work in harmony to deliver relevant search results. Understanding these components is crucial to grasping the overall functionality.
Crawling
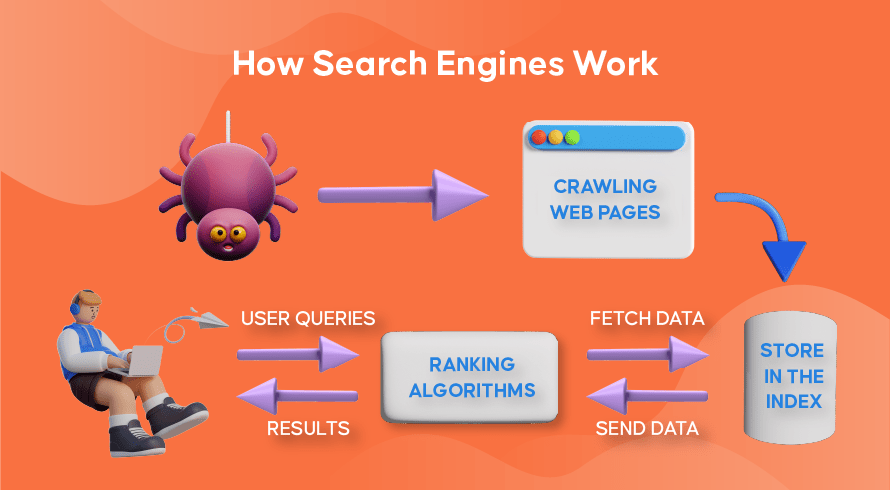
The first step in the process is crawling. Web search engines employ automated programs called “crawlers,” “spiders,” or “bots” to explore the internet. These crawlers follow links from one webpage to another, systematically discovering and indexing new content. They act like digital explorers, mapping the ever-expanding web. The efficiency of a crawler greatly impacts the breadth and depth of the search engine’s index.
Crawlers adhere to certain rules, defined in a file called `robots.txt`, which websites use to instruct crawlers on which pages to index and which to avoid. This is important for managing server load and preventing the indexing of sensitive or irrelevant content. Think of it as a website owner setting boundaries for the search engine’s explorer.
Indexing
Once a crawler discovers a webpage, the content is analyzed and added to the search engine’s index. This process is called indexing. The index is essentially a massive database that stores information about every webpage the search engine has crawled. This includes the words on the page, the links pointing to it, and other relevant metadata.
The indexing process involves parsing the HTML code, extracting text, and identifying keywords. Web search engines use sophisticated algorithms to understand the meaning of the content and its relevance to different search queries. They also consider factors like the frequency of keywords, the structure of the page, and the presence of images and videos. Effective indexing is crucial for quickly retrieving relevant results when a user performs a search.
Ranking
The final step is ranking. When a user enters a search query, the web search engine uses its ranking algorithms to determine the order in which the search results are displayed. These algorithms consider a multitude of factors, including the relevance of the webpage to the query, the authority of the website, and the user’s location and search history.
Ranking algorithms are constantly evolving, as web search engines strive to improve the quality and relevance of their search results. They use machine learning techniques to analyze user behavior and identify patterns that can help them better understand what users are looking for. This ongoing process of refinement ensures that the most relevant and useful results are presented at the top of the search results page.
How Web Search Engines Determine Relevance
Determining relevance is a critical aspect of how web search engines work. It’s not simply about matching keywords; it’s about understanding the intent behind the search query and providing results that are truly helpful to the user.
Keyword Matching
The most basic form of relevance is keyword matching. Web search engines look for webpages that contain the keywords in the search query. However, simple keyword matching is not enough. Search engines also consider the context in which the keywords appear and the overall meaning of the page.
Semantic Analysis
Semantic analysis is a more sophisticated approach to determining relevance. It involves understanding the meaning of words and phrases, as well as the relationships between them. Web search engines use natural language processing (NLP) techniques to analyze the text on a webpage and extract its underlying meaning. This allows them to identify pages that are relevant to the search query even if they don’t contain the exact keywords.
Link Analysis
Link analysis is another important factor in determining relevance. Web search engines consider the number and quality of links pointing to a webpage. A webpage with many high-quality links is considered to be more authoritative and relevant than a webpage with few or no links. This is based on the idea that links are like votes of confidence – the more links a webpage has, the more likely it is to be a valuable resource.
User Experience Signals
Web search engines also use user experience signals to determine relevance. These signals include factors like the click-through rate (CTR) of a search result, the amount of time users spend on a webpage after clicking on it, and the bounce rate (the percentage of users who leave the webpage immediately after arriving). These signals provide valuable insights into how users are interacting with the search results and whether they are finding what they are looking for. If a page has a high bounce rate, it may indicate that the content is not relevant to the search query or that the page is poorly designed.
The Evolution of Search Engine Algorithms
Web search engines have evolved dramatically over the years. Early search engines relied primarily on keyword matching and simple ranking algorithms. However, as the internet has grown and become more complex, search engines have had to adapt and develop more sophisticated techniques.
From Keyword Stuffing to Content Quality
In the early days of search engines, it was possible to manipulate search rankings by stuffing webpages with keywords. This practice, known as keyword stuffing, would trick the search engine into thinking that the page was highly relevant to the search query. However, modern search engines are much more sophisticated and can detect keyword stuffing. They now prioritize content quality and user experience over keyword density.
The Rise of Semantic Search
One of the most significant developments in recent years has been the rise of semantic search. Semantic search is about understanding the meaning of words and phrases, rather than just matching keywords. This has allowed web search engines to provide more relevant and accurate search results.
The Impact of Machine Learning
Machine learning has also had a major impact on how web search engines work. Machine learning algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns and trends that can be used to improve search results. For example, machine learning can be used to personalize search results based on a user’s location, search history, and other factors.
The Future of Web Search Engines
The future of web search engines is likely to be even more personalized and intelligent. Search engines will continue to evolve and adapt to the changing needs of users. Here are some of the trends that are likely to shape the future of search:
Voice Search
Voice search is becoming increasingly popular, as more and more people use voice assistants like Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant. Web search engines will need to adapt to this trend by developing algorithms that can understand and respond to spoken queries.
Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) will play an even greater role in search engines in the future. AI can be used to personalize search results, understand the intent behind search queries, and even generate content automatically.
Visual Search
Visual search is another emerging trend. Visual search allows users to search for information using images instead of text. This can be particularly useful for finding products, identifying objects, or learning more about a particular scene.
Ethical Considerations in Web Search
As web search engines become more powerful, it’s important to consider the ethical implications of their algorithms. Search engines have the power to shape public opinion, influence elections, and even censor information. It’s crucial that search engines are transparent and accountable for their actions.
Bias in Search Results
One of the biggest ethical concerns is bias in search results. Search engine algorithms can be biased in favor of certain viewpoints, which can lead to users being exposed to a skewed or incomplete picture of the world. It’s important for search engines to be aware of these biases and take steps to mitigate them.
Privacy Concerns
Privacy is another important ethical consideration. Web search engines collect vast amounts of data about their users, which can be used to track their online activity and personalize their search results. It’s important for search engines to be transparent about how they collect and use user data and to give users control over their privacy settings.
Conclusion
Web search engines are complex and powerful tools that have revolutionized the way we access information. Understanding how web search engines work is essential for anyone who wants to navigate the digital world effectively. By understanding the core components of a search engine, the factors that determine relevance, and the ethical considerations involved, we can become more informed and empowered users of these invaluable tools. As technology continues to advance, the evolution of search engines will undoubtedly continue, shaping the future of information retrieval and access.
[See also: Search Engine Optimization Basics] [See also: The Future of AI in Search]
