How Web Search Engines Work: A Comprehensive Guide
In today’s digital age, web search engines are indispensable tools. From finding the nearest coffee shop to researching complex scientific topics, we rely on them daily. But have you ever stopped to wonder how web search engines work? This comprehensive guide delves into the intricate processes that allow these powerful systems to deliver relevant results in a fraction of a second. Understanding the mechanics behind how web search engines work not only demystifies the internet but also provides valuable insights for content creators and website owners looking to improve their online visibility. We’ll explore the core components, including crawling, indexing, and ranking, offering a clear and concise explanation of each stage.
The Core Components of a Web Search Engine
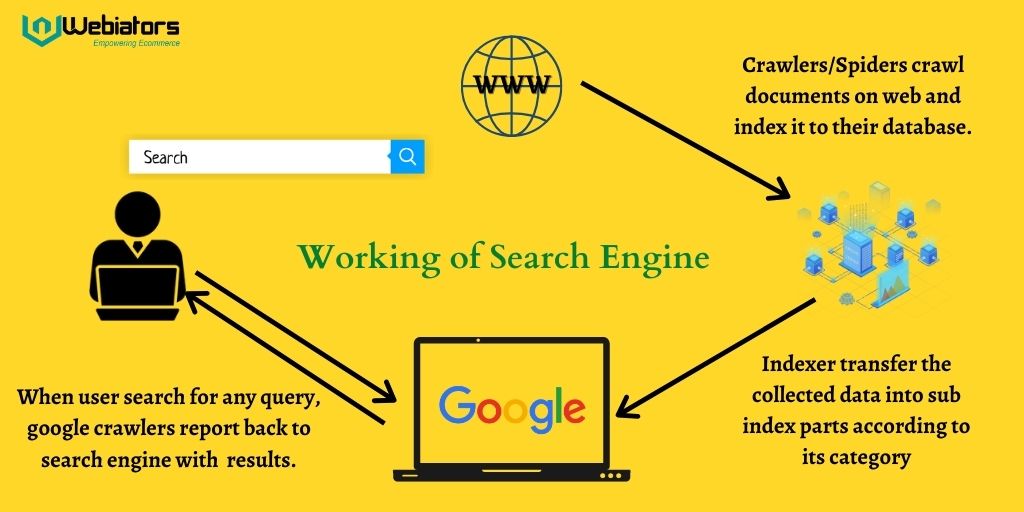
The functionality of web search engines can be broken down into three primary stages: crawling, indexing, and ranking. Each stage is crucial for ensuring users receive the most accurate and relevant search results.
Crawling: Discovering the Web
Crawling, often referred to as spidering, is the process by which web search engines discover and explore the vast landscape of the internet. Search engine crawlers, or spiders, are automated programs that follow links from one webpage to another. Think of it as a digital explorer constantly mapping the internet.
The crawling process begins with a list of known URLs, often referred to as a “seed set.” The crawler visits these URLs and extracts all the links found on those pages. It then adds these new URLs to its queue of pages to visit. This process continues indefinitely, allowing the crawler to discover new content and update its existing knowledge of the web.
Factors that influence crawling include:
- Website Structure: A well-structured website with clear navigation makes it easier for crawlers to access and index content.
- Robots.txt: This file instructs crawlers which parts of the website they are allowed to access.
- Sitemaps: An XML sitemap provides a list of all the important pages on a website, helping crawlers discover content more efficiently.
- Link Structure: Internal and external links play a crucial role in guiding crawlers through the website.
Indexing: Organizing the Information
Once the crawler has discovered a webpage, the next step is indexing. Indexing is the process of analyzing the content of the page and storing it in a structured manner. This allows the web search engine to quickly retrieve relevant information when a user performs a search.
The indexing process involves:
- Content Extraction: The search engine extracts the text, images, and other media from the webpage.
- Parsing: The extracted content is parsed to identify keywords, headings, and other important elements.
- Storage: The parsed information is stored in a massive database, often referred to as the index. This index is designed for fast retrieval of information based on keywords and other criteria.
The index is a critical component of how web search engines work. It allows search engines to quickly identify relevant pages based on a user’s query. Without an efficient index, search engines would be unable to deliver results in a timely manner.
Ranking: Delivering the Best Results
The final stage in the process is ranking. When a user enters a search query, the web search engine uses its ranking algorithms to determine the order in which the search results are displayed. The goal is to present the most relevant and authoritative results at the top of the page.
Ranking algorithms are complex and constantly evolving. They take into account hundreds of factors, including:
- Relevance: How closely the content of the page matches the user’s search query.
- Authority: The credibility and trustworthiness of the website.
- User Experience: Factors such as website speed, mobile-friendliness, and content quality.
- Backlinks: The number and quality of links pointing to the page from other websites.
Search engines use sophisticated machine learning techniques to analyze these factors and determine the ranking of each page. The algorithms are constantly updated to improve the accuracy and relevance of search results. Understanding these ranking factors is essential for anyone looking to improve their website’s visibility in search results.
Advanced Concepts in Web Search Engine Technology
Beyond the core components of crawling, indexing, and ranking, several advanced concepts contribute to the overall functionality of web search engines.
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
NLP is a branch of artificial intelligence that focuses on enabling computers to understand and process human language. Web search engines use NLP to better understand the meaning and intent behind user queries. This allows them to deliver more accurate and relevant results, even when the query is ambiguous or poorly worded.
For example, if a user searches for “best Italian restaurants near me,” the search engine uses NLP to understand that the user is looking for recommendations for Italian restaurants in their local area. It can then use location data and restaurant reviews to provide personalized recommendations.
Machine Learning (ML)
Machine learning is another key technology used by web search engines. ML algorithms are trained on vast amounts of data to identify patterns and make predictions. Search engines use ML to improve their ranking algorithms, personalize search results, and detect spam and other malicious activities.
One example of how ML is used in search is in the development of ranking models. These models are trained on data about user behavior, such as click-through rates and dwell time, to predict which pages are most likely to be relevant and satisfying to users.
Knowledge Graphs
A knowledge graph is a structured database that stores information about entities and their relationships. Web search engines use knowledge graphs to understand the context of search queries and provide more comprehensive and informative results.
For example, if a user searches for “Albert Einstein,” the search engine can use its knowledge graph to provide information about Einstein’s life, work, and accomplishments. It can also provide links to related topics, such as physics and relativity.
The Future of Web Search Engines
Web search engines are constantly evolving to meet the changing needs of users. Several trends are shaping the future of search, including:
Voice Search
With the rise of voice assistants like Siri and Alexa, voice search is becoming increasingly popular. Web search engines are adapting to this trend by optimizing their algorithms for spoken queries. This requires a deeper understanding of natural language and the ability to handle conversational search queries.
Mobile Search
Mobile devices now account for a significant portion of web traffic. Web search engines are prioritizing mobile-friendly websites and optimizing their search results for mobile users. This includes factors such as website speed, mobile responsiveness, and content readability on small screens.
Personalized Search
Web search engines are increasingly personalizing search results based on user data, such as location, search history, and browsing behavior. This allows them to deliver more relevant and tailored results to each individual user. However, personalization also raises concerns about privacy and filter bubbles.
Visual Search
Visual search allows users to search for information using images instead of text. Web search engines are developing advanced image recognition technologies to understand the content of images and provide relevant search results. This opens up new possibilities for searching for products, identifying landmarks, and discovering information about the world around us.
Optimizing for Web Search Engines
Understanding how web search engines work is crucial for website owners and content creators who want to improve their online visibility. Here are some key strategies for optimizing your website for search engines:
- Keyword Research: Identify the keywords that your target audience is using to search for information related to your business.
- On-Page Optimization: Optimize your website’s content, title tags, and meta descriptions with relevant keywords.
- Off-Page Optimization: Build high-quality backlinks from other reputable websites.
- Technical SEO: Ensure your website is technically sound, with fast loading speeds, mobile-friendliness, and a clear site structure.
- Content Marketing: Create valuable and engaging content that attracts and retains your target audience.
By implementing these strategies, you can improve your website’s ranking in search results and drive more traffic to your site. Remember that SEO is an ongoing process that requires continuous effort and adaptation to the ever-changing landscape of web search engines.
Conclusion
Web search engines are complex and sophisticated systems that play a vital role in our digital lives. By understanding how web search engines work, we can appreciate the incredible technology that powers these tools and learn how to optimize our online presence for better visibility. From crawling and indexing to ranking and advanced technologies like NLP and machine learning, the world of search is constantly evolving. Staying informed about these changes is essential for anyone who wants to succeed in the online world. [See also: SEO Best Practices for 2024] [See also: The Ultimate Guide to Keyword Research] [See also: How to Improve Your Website’s Ranking on Google]
